Tensorflow神经网络框架(第三课 3-1Tensorflow简单实例 非线性回归 梯度下降法)
本文共 1358 字,大约阅读时间需要 4 分钟。
 Logout
Logout In [1]:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
In [2]:
#使用numpy生成200个随机点
x_data = np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,200)[:,np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0,0.02,x_data.shape)#生成随机噪声
y_data = np.square(x_data) + noise
#定义两个placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
#定义神经网络中间层
Weights_L1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1,10]))
biases_L1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10]))
Wx_plus_b_L1 = tf.matmul(x,Weights_L1) + biases_L1
L1 = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L1) #中间层的输出
#定义神经网络输出层
Weights_L2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10,1]))
biases_L2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,1]))
Wx_plus_b_L2 = tf.matmul(L1,Weights_L2) + biases_L2
prediction = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L2) #预测的结果
#二次代价函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - prediction)) #真实值 - 预测值 平方
#使用梯度下降法
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for _ in range(2000):
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={ x:x_data,y:y_data}) #获取预测值
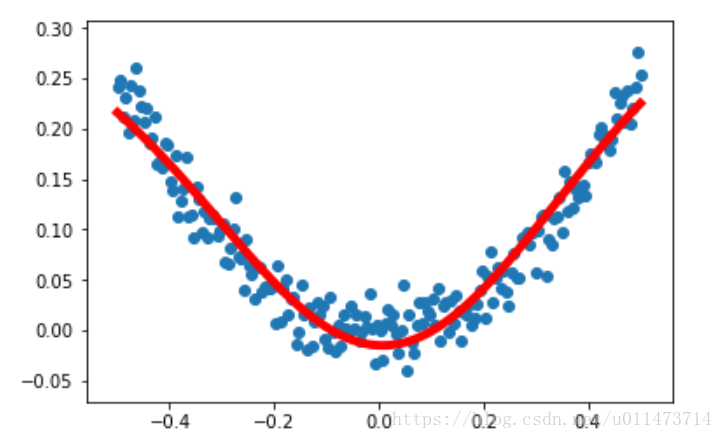
prediction_value = sess.run(prediction,feed_dict={ x:x_data}) #画图
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data)
plt.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'r-',lw=5)
plt.show()
你可能感兴趣的文章
ES相关度评分
查看>>
我们一起做一个可以商用的springboot脚手架
查看>>
idea在搭建ssm框架时mybatis整合问题 无法找到mapper
查看>>
java设计基本原则----单一职责原则
查看>>
HashMap的实现
查看>>
互斥锁 synchronized分析
查看>>
java等待-通知机制 synchronized和waity()的使用实践
查看>>
win10 Docke安装mysql8.0
查看>>
docker 启动已经停止的容器
查看>>
order by 排序原理及性能优化
查看>>
Lock重入锁
查看>>
docker安装 rabbitMq
查看>>
git 常用命令 入门
查看>>
linux安装docker
查看>>
关闭selinx nginx无法使用代理
查看>>
shell 脚本部署项目
查看>>
spring cloud zuul网关上传大文件
查看>>
springboot+mybatis日志显示SQL
查看>>
工作流中文乱码问题解决
查看>>
maven打包本地依赖包
查看>>